1. Introduction to Bitcoin
- Bitcoin (BTC, symbol ₿) is the first decentralized cryptocurrency.
- It functions as a digital currency that operates without central banks or governments.
- Bitcoin enables secure, peer-to-peer internet transactions through blockchain technology.
2. How Bitcoin Started
- Invented in 2008 by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto.
- White paper published on October 31, 2008: “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”
- Network launched January 3, 2009, with the mining of the “genesis block.”
- Early adoption milestones include the famous “Bitcoin Pizza Day” in May 2010.
3. How Bitcoin Works
- Transactions are verified by network nodes via cryptography and recorded in a public blockchain.
- Mining validates transactions and creates new bitcoins, capped at 21 million total.
- Bitcoin is pseudonymous, linked to public keys rather than identities.
4. Bitcoin’s Growth and Price Evolution
- Bitcoin’s journey: negligible value early on to surpassing $118,000 in 2025.
- Major milestones: $1,000 in 2013, nearly $19,000 in 2017, over $64,000 in 2021, crossing $100,000 in late 2024.
- Bitcoin now serves as a digital store of value, akin to “digital gold.”
Bitcoin Price Growth Chart 2009–2025
The following chart visually represents Bitcoin’s historic price growth over the years, illustrating its rise from virtually zero to over $118,000 in 2025:
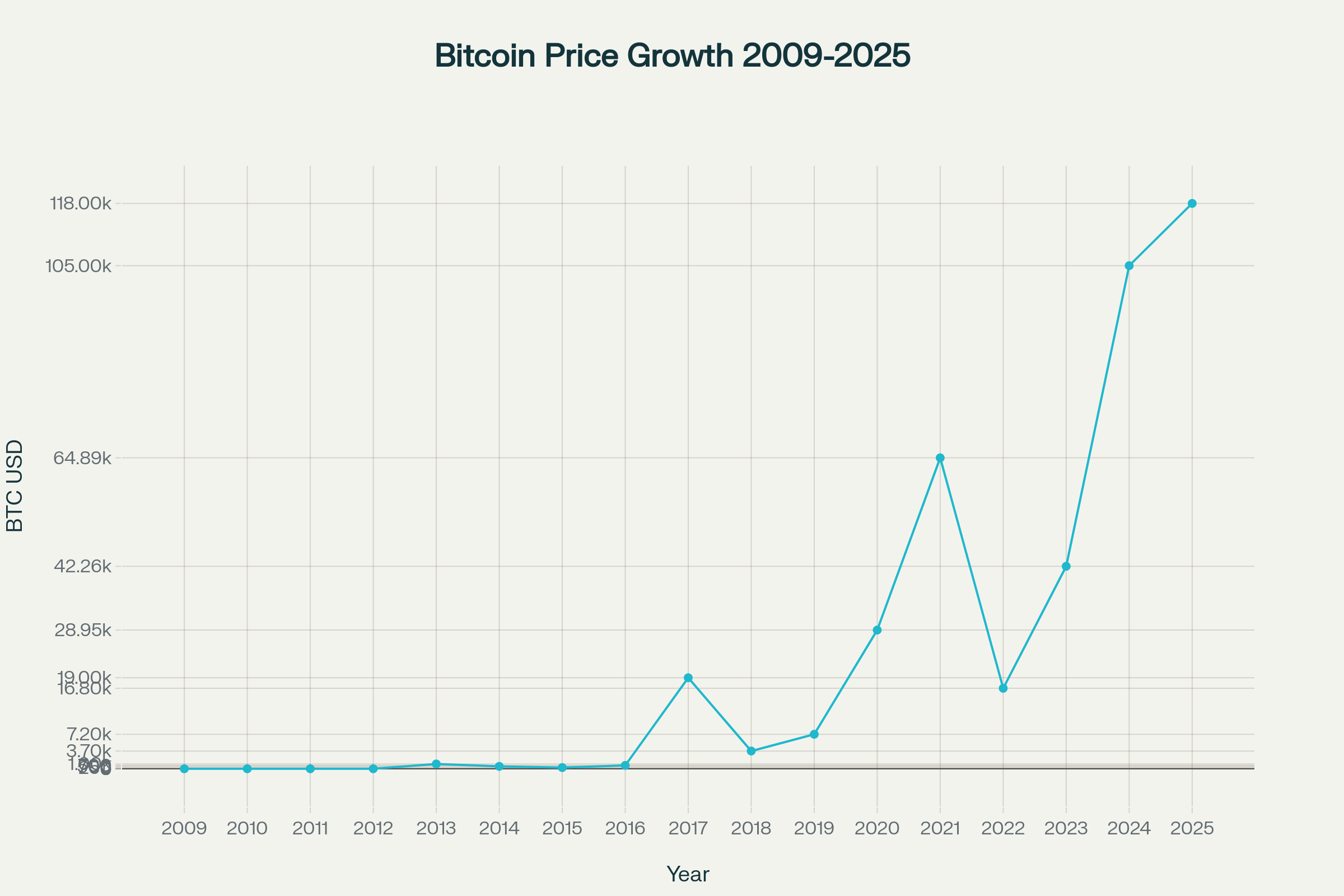
Bitcoin Price Growth from 2009 to 2025 in USD
| Year | Approximate Bitcoin Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| 2009 | $0.0 |
| 2010 | $0.1 |
| 2011 | $1.0 |
| 2012 | $5.0 |
| 2013 | $1,000 |
| 2014 | $500 |
| 2015 | $250 |
| 2016 | $700 |
| 2017 | $19,000 |
| 2018 | $3,700 |
| 2019 | $7,200 |
| 2020 | $28,949 |
| 2021 | $64,895 |
| 2022 | $16,800 |
| 2023 | $42,258 |
| 2024 | $105,000 |
| 2025 | $118,000 |
5. Why People Hold Bitcoin
- As an investment aiming for appreciation.
- To store value amid fiat currency inflation concerns.
- To use as a decentralized means of transferring value globally.
- To participate in innovative financial technology.
6. How to Buy Bitcoin
- Choose reputable exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, or CoinDCX.
- Complete identity verification (KYC) per legal requirements.
- Deposit fiat currency via bank or card.
- Purchase Bitcoin via market or limit orders.
- Optionally transfer to secure personal wallets for better control.
- Use strong security practices such as two-factor authentication and hardware wallets.
7. Additional Key Points
- Bitcoin transactions are irreversible—double-check recipient details.
- Mining rewards halve roughly every four years; latest halving was in April 2024.
- The Bitcoin network is secure but energy-intensive.
- Adoption and regulation vary globally, with growing acceptance and some restrictions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Bitcoin
- What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows peer-to-peer payments over the internet without a middleman. - How do I store Bitcoin safely?
Use digital wallets—software wallets for convenience or hardware wallets for enhanced security—and always keep your private keys secure. - Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin’s legality varies by country, with some accepting and regulating it, while others restrict or ban its use. - Why is Bitcoin’s price so volatile?
It is driven by supply and demand, market sentiment, regulation news, adoption rates, and macroeconomic factors. - How many bitcoins will exist?
The maximum supply is capped at 21 million bitcoins, making it deflationary and scarce.
Investment Tips for Bitcoin in 2025
- Do thorough research before investing.
Understand Bitcoin’s fundamentals, market trends, and risks. - Choose regulated, trusted exchanges for buying and selling.
- Keep security a top priority.
Use hardware wallets and two-factor authentication. - Avoid investing more than you can afford to lose due to volatility.
- Consider dollar-cost averaging to mitigate price swings.
- Stay updated on regulatory changes worldwide, especially in your country.
Bitcoin Glossary: Key Terms to Know
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first cryptocurrency, created in 2009, representing a digital form of money.
- Blockchain: A public, immutable ledger recording all Bitcoin transactions.
- Mining: The process of validating transactions and securing the network, rewarded by new bitcoins.
- Wallet: Software or hardware tool to store Bitcoin private keys safely.
- Private Key: A secret cryptographic key that controls access to your bitcoins.
- Public Key: The address others use to send you Bitcoin.
- Halving: An event that halves the mining rewards roughly every four years, reducing new Bitcoin supply.
- Satoshi: The smallest unit of Bitcoin, equal to 0.00000001 BTC.
- Exchange: A platform where you can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, legal, or tax advice. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are highly volatile and speculative assets, and their values can fluctuate significantly. Before making any investment or financial decisions related to Bitcoin, you should conduct your own research and consult with licensed professionals tailored to your individual circumstances.
Past performance is not indicative of future results. Cryptocurrency investments carry risks, including loss of principal. Always use caution, secure your digital assets properly, and be aware of local regulations regarding cryptocurrency transactions.


1 thought on “What Is Bitcoin? A Comprehensive Guide”
Comments are closed.